Goal
- @Autowired에 대해 알아본다
- 해당 타입의 빈이 없거나 하나인 경우, @Autowired의 동작
- 해당 타입의 빈이 여러개인 경우, @Autowired의 동작
- @Autowired의 동작원리를 알아본다
@Autowired 란?
필요한 의존 객체의 "타입"에 해당하는 빈을 찾아 주입하며, 기본 값은 (required=true) 못 찾으면 어플리케이션 구동이 실패한다.
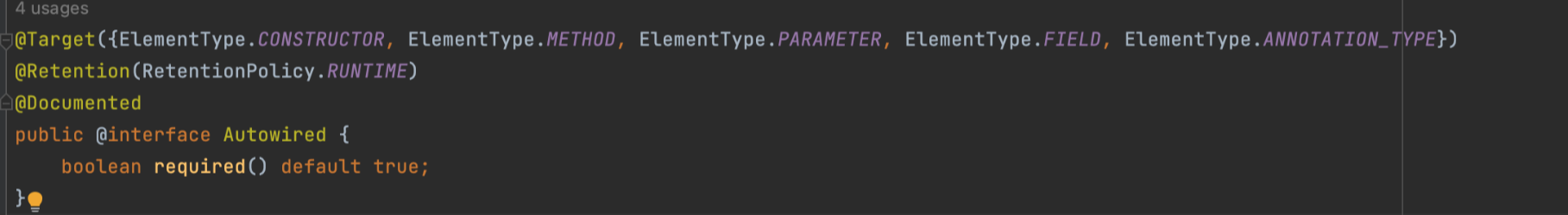
해당 타입의 빈이 없거나 하나인 경우 @Autowired의 동작
1. 생성자
@Service
public class BookService {
BookRepository bookRepository;
@Autowired
public BookService(BookRepository bookRepository) {
this.bookRepository = bookRepository;
}
}// bean 등록 x
public class BookRepository {
}결과
***************************
APPLICATION FAILED TO START
***************************
Description:
Parameter 0 of constructor in com.example.demosping51.BookService required a bean of type 'com.example.demosping51.BookRepository' that could not be found.
Action:
Consider defining a bean of type 'com.example.demosping51.BookRepository' in your configuration.
=> bookService의 생성자에 0번째 파라미터로 세팅한 bookRepository에 해당하는 bean이 없으므로 bean으로 등록하라
// bean 등록 o
@Repository
public class BookRepository {
}결과
문제 없이 어플리케이션 실행
정리
생성자 의존성 주입은 bean을 만들 때에도 개입이 된다. 해당하는 생성자에 전달받아야 하는 타입에 bean이 없다면 인스턴스를 만들지 못하고, bookService도 등록이 안됨
2. setter
@Service
public class BookService {
BookRepository bookRepository;
@Autowired
public void setBookRepository(BookRepository bookRepository) {
this.bookRepository = bookRepository;
}
}public class BookRepository {
}결과
Description:
Parameter 0 of method setBookRepository in com.example.demosping51.BookService required a bean of type 'com.example.demosping51.BookRepository' that could not be found.
Action:
Consider defining a bean of type 'com.example.demosping51.BookRepository' in your configuration.
@Autowired(required=false)
public void setBookRepository(BookRepository bookRepository) {
this.bookRepository = bookRepository;
}결과
문제 없이 어플리케이션 실행
정리
생성자 주입과 달리 bookService 인스턴스 자체는 만들 수 있다. 그러나 @Autowired에 따라 어플리케이션이 실행여부가 달라진다.
@Autowired가 있을 경우, required=false로 세팅하면 옵션이기 때문에 어플리케이션이 구동된다. 그러나 따로 설정하지 않으면 기본값은 required=true이기 때문에 구동되지 않는다.
3. 필드
@Service
public class BookService {
@Autowired(required = false)
BookRepository bookRepository;
}결과
문제 없이 어플리케이션 실행
정리
@Autowired를 optional로 설정하여 bookService가 해당하는 의존성 없이도 등록이 가능하다
해당 타입의 빈이 여러개인 경우 @Autowired의 동작
사용할 빈을 명시 x
public interface BookRepository {
}@Repository
public class RoiseRepository implements BookRepository{
}
@Repository
public class KimRepository implements BookRepository{
}@Service
public class BookService {
@Autowired
BookRepository bookRepository;
}결과
***************************
APPLICATION FAILED TO START
***************************
Description:
Field bookRepository in com.example.demosping51.BookService required a single bean, but 2 were found:
- kimRepository: defined in file [/Users/daseulkim/Desktop/portfolio/demosping51/target/classes/com/example/demosping51/KimRepository.class]
- roiseRepository: defined in file [/Users/daseulkim/Desktop/portfolio/demosping51/target/classes/com/example/demosping51/RoiseRepository.class]
Action:
Consider marking one of the beans as @Primary, updating the consumer to accept multiple beans, or using @Qualifier to identify the bean that should be consumed
=> repository에 해당하는 bean이 두개가 발견이 되었는데, 둘중에 어떤 걸 주입해야 할지 모르겠어서 에러가 났으니
1. @Primary 어노테이션을 통해 어느 bean을 사용하고 싶은지 마킹하거나, 2. @Qualifier을 사용하거나, 3. 모든 bean을 다 받아라
1. @Primary
@Repository @Primary
public class RoiseRepository implements BookRepository{
}
@Repository
public class KimRepository implements BookRepository{
}결과
문제 없이 어플리케이션 실행
// 클래스 확인용 Runner
@Component
public class BookServiceRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Autowired
BookService bookService;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
bookService.printBookRepository();
}
}@Service
public class BookService {
@Autowired
BookRepository bookRepository;
public void printBookRepository(){
System.out.println(bookRepository.getClass());
}
}결과
class com.example.demospring51.RosieRepository
정리
bookService에서는 bookRepository를 주입 시,@Primary가 있는 bean을 주입한다.
@Qualifier보다 type safe 하다
2. @Qualifier
@Service
public class BookService {
@Autowired @Qualifier("roiseRepository")
BookRepository bookRepository;
public void printBookRepository(){
System.out.println(bookRepository.getClass());
}
}결과
class com.example.demospring51.RosieRepository
정리
@Qualifier에 빈의 id (= camel 기법의 클래스 이름)를 적어 해당 bean을 주입한다.
@Primary보다 type safe 하지 않다.
3. 모든 bean을 받기
@Service
public class BookService {
@Autowired
List<BookRepository> bookRepositories;
public void printBookRepository(){
this.bookRepositories.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}결과
com.example.demosping51.KimRepository@a7ad6e5
com.example.demosping51.RoiseRepository@3b1ed14b
@Autowired의 동작 원리
라이프 사이클
BeanPostProcessor 라이프 사이클 인터페이스 구현체에 의해서 동작한다
BeanPostProcessor (Spring Framework 6.0.11 API)
postProcessAfterInitialization Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance after any bean initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's afterPropertiesSet or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values
docs.spring.io
BeanPostProcessor
1. bean initialization 빈 생성
2. bean 인스턴스 생성
3. bean initialization 라이프사이클 이전 / 이후 부가적인 작업을 하는 또 다른 라이프사이클 콜백 (ex. @PostConstruct, InitializingBean 인터페이스)
그 중에서도 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor가 처리를 해주는 것!
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor (Spring Framework 6.0.11 API)
postProcessProperties Post-process the given property values before the factory applies them to the given bean. The default implementation returns the given pvs as-is. Specified by: postProcessProperties in interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor P
docs.spring.io
참고
스프링입문 강의 by 백기선
https://www.inflearn.com/course/lecture?courseSlug=spring&unitId=15538 https://www.inflearn.com/course/spring_revised_edition/dashboard
https://www.inflearn.com/course/spring_revised_edition/dashboard
'Spring > about spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [IoC 컨테이너와 빈] 빈의 스코프 (0) | 2023.07.22 |
|---|---|
| [IoC 컨테이너와 빈] @Component Scan (0) | 2023.07.22 |
| [IoC 컨테이너와 빈] ApplicationContext (0) | 2023.07.19 |
| [스프링 삼각형] PSA 잘 만든 인터페이스 (0) | 2023.07.17 |
| [스프링 삼각형] AOP 관점 지향 프로그래밍 (0) | 2023.07.11 |
